In the field of real estate development, the interplay between the right to light and the right to build can lead to complex scenarios that require thoughtful consideration. Right to light surveys are crucial in understanding the relationship between these rights, notably in crowded city environments where space is at a premium. Understanding the nuances of these rights is vital for developers, homeowners, and legal professionals alike, because not addressing light rights can lead to costly disputes and project delays.
As urban areas develop and grow, the value of daylight in our homes and workplaces has become increasingly important. This piece examines the idea of surveys regarding light rights, analyzing their legal framework, the survey process, and their impact on real estate development. By looking at various case studies and frequent cases, our goal is to shed light on the path for developers navigating these often-overlooked rights, ensuring the safeguarding of their interests in addition to those of adjacent properties.
Comprehending Right to Light
The right to light is a juridical doctrine that grants landowners the privilege to get natural sunlight through defined openings in their properties, typically glass panes. This right has deep roots in traditional law and is designed to preserve the light entry of existing structures against any likely obstructions that new developments may create. Real estate holders who have experienced a certain amount of light for a specified time may assert this right, and it is important for both current property owners and builders to understand the ramifications of this privilege.
In the UK, the principles governing right to light have developed over the years, with laws and judicial precedents helping to shape how these rights are validated and upheld. Generally, this entitlement is recognized when a property has had clear light for a period of two decades. The assessment of whether a development violates on someone’s right to light takes into account factors such as the direction and intensity of light that a property get. Contractors must handle these entitlements cautiously to circumvent legal disputes that can arise from blocking neighboring properties.
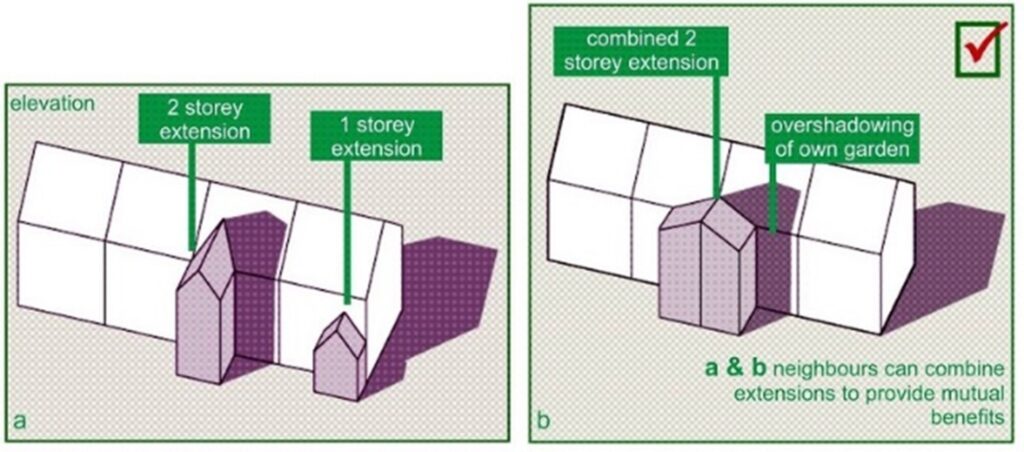
Light right considerations have become important in property development, particularly in metropolitan areas where space is restricted, and buildings are constructed in adjacency to each other. Builders must engage in thorough assessments and inspections to ascertain any likely impacts on neighboring rights to light during the planning stages of their initiatives. Understanding the nuances of light rights can eventually aid in attaining favorable development results while lessening conflicts with adjacent property owners.
Legal Consequences and Adherence
Comprehending the legal consequences of light rights is essential for developers and landowners alike. The light rights is a lawful easement that grants a property owner the right to obtain natural light through openings and openings in their structures. If a new construction obstructs existing light, it can lead to disputes and possible legal action. Non-compliance with right to light regulations can result in costly litigation and setbacks in construction timelines.
When it comes to adherence, developers must ensure that their projects comply to established regulations and standards concerning light access. This includes conducting thorough light rights assessments before starting any construction. By securing a detailed assessment, developers can identify possible issues early and reduce risks associated with obstructing a neighbor's light. Failing to tackle these matters during the planning stages can jeopardize not only the project's outcome but also lead to significant monetary repercussions.
Integrating right to light assessments into the development process is essential for avoiding legal disputes. Knowledge of the lawful landscape related to light rights and the actions required for adherence can foster positive relationships with neighboring properties. Consulting with legal experts and depending on professional right to light reports ensures that projects are not only compliant but also considerate of existing rights, ultimately facilitating smoother project execution.
Procedure and Case Studies
The process of performing a Right to Light survey generally begins with an initial evaluation of the site and its surroundings. Surveyors evaluate current light conditions and identify potential issues that could arise due to upcoming developments. This involves measuring the angle of sunlight and determining the amount of daylight available to neighboring properties. Utilizing specific tools and techniques, such as sunlight and daylight modeling, surveyors gather crucial data that informs their analysis and outcomes.
Case examples reveal the complexities developers face when dealing with Right to Light issues. For instance, in a crowded urban setting, one particular case involved a developer whose proposed building obstructed a neighbor's ability to light, resulting in significant objections. To address this, the developer hired a detailed Right to Light survey, which showed the extent of the light infringement. more information facilitated negotiations that ultimately resulted in design alterations, permitting the project to proceed while reducing impact on neighboring properties.
Another example demonstrates how a developer successfully resolved a Right to Light dispute involving a historic building. By involving experts and following the BRE guidelines, the developer was able to implement strategies that respected the light rights of current structures. The collaboration not only led to a successful development but also showcased the importance of early Right to Light assessments in preventing costly legal battles and ensuring harmonious community relations.
